Priority Health Issues
Hepatitis B Virus (HBV)
Dallas County Health and Human Services - 2377 N. Stemmons Freeway, Dallas, TX 75207
Telephone: 214-819-2000
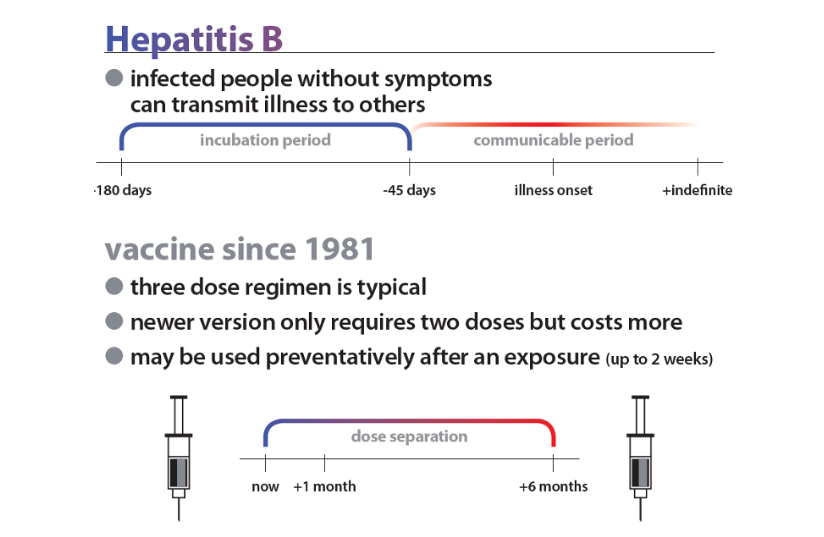
Hepatitis B is a contagious liver disease that is caused by the Hepatitis B virus. Hepatitis B is transmitted through contact with blood or bodily fluids such as semen or vaginal fluids. Many people can carry the virus without noticeable symptoms for years, but if left untreated, it may lead to liver complications over time. To stay proactive, the CDC recommends that all adults over 18 get tested for Hepatitis B. Testing both before and after vaccination helps confirm immunity and ensures you are not a carrier.

DCHHS division offers additional education about Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) and initial screenings. Appointments are required for testing. Screening tests are $35. For information, consultation or to make an appointment, call (214) 819-2004.
The best way to protect against Hepatitis B virus is to get the vaccine. DCHHS provides vaccines for adults and children. Please see below for details.
DCHHS Clinics Vaccination and Prevention
Children
DCHHS provides vaccines for children at the main clinic located at:
2377 N. Stemmons Freeway
Dallas, TX 75207
For more information call (214) 819-2163.
DCHHS also provides vaccines for children only at clinics in the community.
Adults
DCHHS provides vaccines for adults at the International Travel office located:
2377 N. Stemmons Freeway
Dallas, TX 75207
For more information call (214) 819-2162.
Note: In case the numbers are not working, please call the phone bank at (972) 692-2780.
What are the different forms of Hepatitis B infection?
- Acute Hepatitis B virus infection: a short-term illness that occurs within the first 6 months after someone is exposed to the Hepatitis B virus. Acute infection can lead to chronic infection
- Chronic Hepatitis B virus infection: a long-term illness that occurs when the Hepatitis B virus remains in a person’s body
Hepatitis B is spread when blood, semen, or other body fluid infected with the Hepatitis B virus enters the body of a person who is not infected. People can become infected with the virus during activities such as:
- Birth (spread from an infected mother to her baby during birth)
- Sex with an infected partner
- Sharing needles, syringes, or other drug-injection equipment
- Sharing items such as razors or toothbrushes with an infected person
- Direct contact with the blood or open sores of an infected person
- Exposure to blood from needlesticks or other sharp instruments
Who is at risk for Hepatitis B?
Although anyone can get Hepatitis B, some people are at greater risk, such as those who:
- Have sex with an infected person
- Have multiple sex partners
- Have a sexually transmitted disease
- Are men who have sexual contact with other men
- Inject drugs or share needles, syringes, or other drug equipment
- Live with a person who has chronic Hepatitis B
- Are infants born to infected mothers
- Are exposed to blood on the job
- Are hemodialysis patient
- Travel to countries with moderate to high rates of Hepatitis B
What are the symptoms of acute Hepatitis B?
Symptoms of acute Hepatitis B, if they appear, can include:
- Fever
- Fatigue
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Abdominal pain
- Dark urine
- Clay-colored bowel movements
- Joint pain
- Jaundice (yellow color in the skin or the eyes)
How can you prevent Hepatitis B?
The best way to prevent Hepatitis B is by getting the Hepatitis B vaccine. The Hepatitis B vaccine is safe and effective and is usually given as 3–4 shots during a 6-month period.
Who should be vaccinated against Hepatitis B?
Hepatitis B vaccination is recommended for:
- All infants, starting with the first dose of Hepatitis B vaccine at birth.
- All children and adolescents younger than 19 years of age who have not been vaccinated.
- People whose sex partners have Hepatitis B.
- Sexually active persons who are not in a long-term, mutually monogamous relationship.
- Persons seeking evaluation or treatment for a sexually transmitted disease.
- Men who have sexual contact with other men.
- People who share needles, syringes, or other drug-injection equipment.
- People who have close household contact with someone infected with the Hepatitis B virus.
- Health care and public safety workers at risk for exposure to blood or blood-contaminated body fluids on the job.
- People with end-stage renal disease, including predialysis, hemodialysis, peritoneal dialysis, and home dialysis patients.
- Residents and staff of facilities for developmentally disabled persons.
- Travelers to regions with moderate or high rates of Hepatitis B.
- People with chronic liver disease.
- People with HIV infection.
- Anyone who wishes to be protected from Hepatitis B virus infection.
- For more details about Hepatitis B Virus, please visit DCHHS Communicable Diseases.
- If you have concerns or symptoms, please consult your doctor for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate care.
QUICK LINKS
LOCATIONS
EMPLOYEES
-
You must be on the network to see these links.





